Factbook
Monomers
The Monomers division supplies a broad portfolio of large-volume monomers, basic polymers and inorganic chemicals. Major products include MDI (methylene diphenyl diisocyanate), TDI (toluene diisocyanate), propylene oxide, caprolactam, adipic acid, HMD (hexamethylenediamine), ammonia, polyamide 6 and 6.6, nitric acid, sulfur and chlorine products, inorganic salts, urea, glues and impregnating resins. The products are used in a broad spectrum of industries, such as automotive, furniture, construction, woodworking, food, pharmaceuticals, feed, solar, packaging and textiles. By providing a circular or low product carbon footprint (PCF) option in every major product line, the Monomers division is in a key position to drive the sustainable transformation of the various industries it serves.
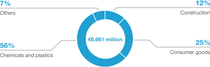
Sales by direct customer industry 2024
Portfolio
Ammonia-based chemicals
In the ammonia value chain, BASF provides ammonia, urea and AdBlue®. The production of liquid CO2 is also part of this value chain.
Ammonia is a key component in BASF’s production Verbund. It is an important raw material for urea as well as many other products such as nitric acid, amines and isocyanates. BASF uses urea as a raw material to produce both glues and AdBlue®, a high purity urea solution that is used in trucks and passenger cars to reduce NOx emissions from diesel engines.
BASF offers various biomass-balanced (BMB) options within its ammonia value chain, including ammonia anhydrous BMBcert™, ammonia solution 24.5% BMBcert™, urea prills BMBcert™, urea solution 40% BMBcert™ and urea solution 45% BMBcert™.
Glues and impregnating resins
BASF is the inventor of Kaurit® and Kauramin® glues, two well-known brands in the wood-working industry. For both products, BASF offers a LowPCF option produced with renewable electricity as well as a biomass balance option based on biomethane and renewable electricity. BASF’s glues and impregnating resins can be used for different types of panel boards and laminated flooring. The portfolio encompasses liquid and powder glues specifically developed to produce a broad range of wood-based materials that meet low-emission standards. Powder glues are also used in other industries, for example, to produce clutch linings in vehicles. BASF’s impregnating resins have been designed for the treatment of various papers, including overlay, counterbalance and decor papers for the flooring or furniture industry.
Inorganic chemicals
Inorganic chemicals are mainly used as precursors for plastics, amines and other high-value chemicals. The product portfolio ranges from basic chemicals to inorganic salts and includes ammonium salts, caustic soda, chlorine, nitric acid, standard alcoholates and sulfuric acid.
BASF is one of the leading suppliers of sodium nitrate (a component for storage media for solar thermal power applications), sodium methylate (a catalyst and reactant for the production of biodiesel and in the pharma and agricultural industry) and a variety of inorganic salts for different industries such as food, feed, textiles and paper.
Isocyanates and propylene oxide
BASF is a world leader in isocyanates, which are key components to produce soft or rigid foams. The company’s isocyanate portfolio offers customers a broad range of MDI and TDI grades. MDI is a versatile isocyanate for the production of flexible foams as well as semi-rigid and rigid polyurethane plastics. Its primary applications are construction, consumer appliances, automotive components and shoe soles. TDI is an isocyanate used primarily in the manufacturing of flexible foams. Its main applications include mattresses and cushions for furniture and automotive seating.
Propylene oxide is the main raw material for polyether polyols. Polyols are – together with isocyanates – the second key component for polyurethane foams. Other applications for propylene oxide are propylene glycols, surfactants and amines.
Polyamides and precursors
BASF is the world’s leading supplier of high-quality polyamides, with the trade name Ultramid®, and polyamide precursors such as caprolactam, HMD and adipic acid. BASF offers a wide product range of polyamides for injection molding and extrusion. The product range includes polyamide 6 grades (Ultramid® B), polyamide 6.6 grades (Ultramid® A), special grades based on copolyamides (Ultramid® C) as well as Ultramid® Ccycled®, which is produced using recycled plastic waste or end-of-life tires and biomass-balanced Ultramid® derived from renewable raw materials.
Polyamides from BASF are the materials of choice for many applications:
- Engineering plastics: Ultramid® is used to produce molding compounds. Due to their outstanding properties, the various Ultramid® grades have become indispensable in almost all fields of engineering for the most varied components and machine parts for the automotive industry, as high-quality electrical insulating materials and for many special applications.
- Films for food packaging: Ultramid® is especially well-suited for the packaging sector due to its high strength, outstanding thermoformability, high thermal stability and very good barrier properties toward gases, especially oxygen, flavors and aromas.
- Textiles: With loopamid®, BASF offers a polyamide 6 that is entirely made from textile waste, thus closing the loop for polyamide 6 garments. Additionally, BASF’s variety of polyamide 6 grades for textiles enable the manufacturing of superior quality textiles, e.g., for swimwear and high-tech outdoor garments as well as high-end polyamide carpets and technical fiber applications.
Market position and main competitors
The Monomers division holds one of the top three market positions in around three-quarters of the strategic business areas in which it is active.
The main competitors (alphabetical order) include AdvanSix, Ascend, Covestro, Dow, Envalior, Grupa Azoty, Huntsman, Ube and Wanhua.
Focus of research and development
R&D efforts are focused on process innovation to optimize the division’s large asset base as well as the development of new products and applications to support the green transformation of the various customer industries it serves.
Acquisitions/JVs/investments
From 2022 onward
| Product group | Description | Year |
| Alcoholates | New alcoholates plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany | 2027 |
| HMD | New world-scale plant in Chalampé, France | 2024 |
| MDI | Expansion of production in Geismar, Louisiana (staggered investment approach) | 2020-2026 |
| Polyamide 6.6 | BASF intends to take over DOMO Chemicals’ 49% share in the Alsachimie joint venture in Chalampé, France, to gain full ownership | 2025 |
Divestitures/shutdowns
From 2022 onward
| Product group | Description | Year |
| Adipic acid value chain | Closure of the adipic acid plant, the plant for the precursors cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone, and the soda ash plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany | 2023–2026 |
| Ammonia value chain | Closure of one of two ammonia plants, the melamine plant and the ammonium sulfate nitrate fertilizer plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany | 2023 |
| Closure of the caprolactam plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany | 2023–2026 | |
| TDI | Closure of the TDI complex in Ludwigshafen, Germany | 2023 |
Major nameplate capacities of BASF1
Thousand metric tons per year
| Product group | Capacity |
| Adipic acid | 620 |
| Ammonia | 1,370 |
| Caprolactam | 600 |
| Chlorine | 495 |
| Isocyanates | 2,400 |
| Polyamides 6 and 6.6 | 885 |
| Propylene oxide | 675 |
| Sulfuric acid | 920 |
| Urea | 545 |
1 All capacities are included at 100%, including plants belonging to joint operations and joint ventures.
Innovation

Cavipor® clay foam for building insulation
With Cavipor®, BASF has developed the world’s first clay foam solution for energetic optimization of buildings. The unique in-situ foam system consists of three water-based components and air. It combines the advantages of a mineral-based insulation material with the simple, safe and clean applicability of a foam system. It is non-combustible, recyclable, easy to process, and its water-based components can be handled completely dust- and fiber-free. When a Cavipor®-insulated building is demolished at the end of its lifetime, the foam can be disposed of together with construction waste or reused as foundation material. In addition, waste foam can be reused by replacing up to 10% of raw materials in production of new Cavipor® components.